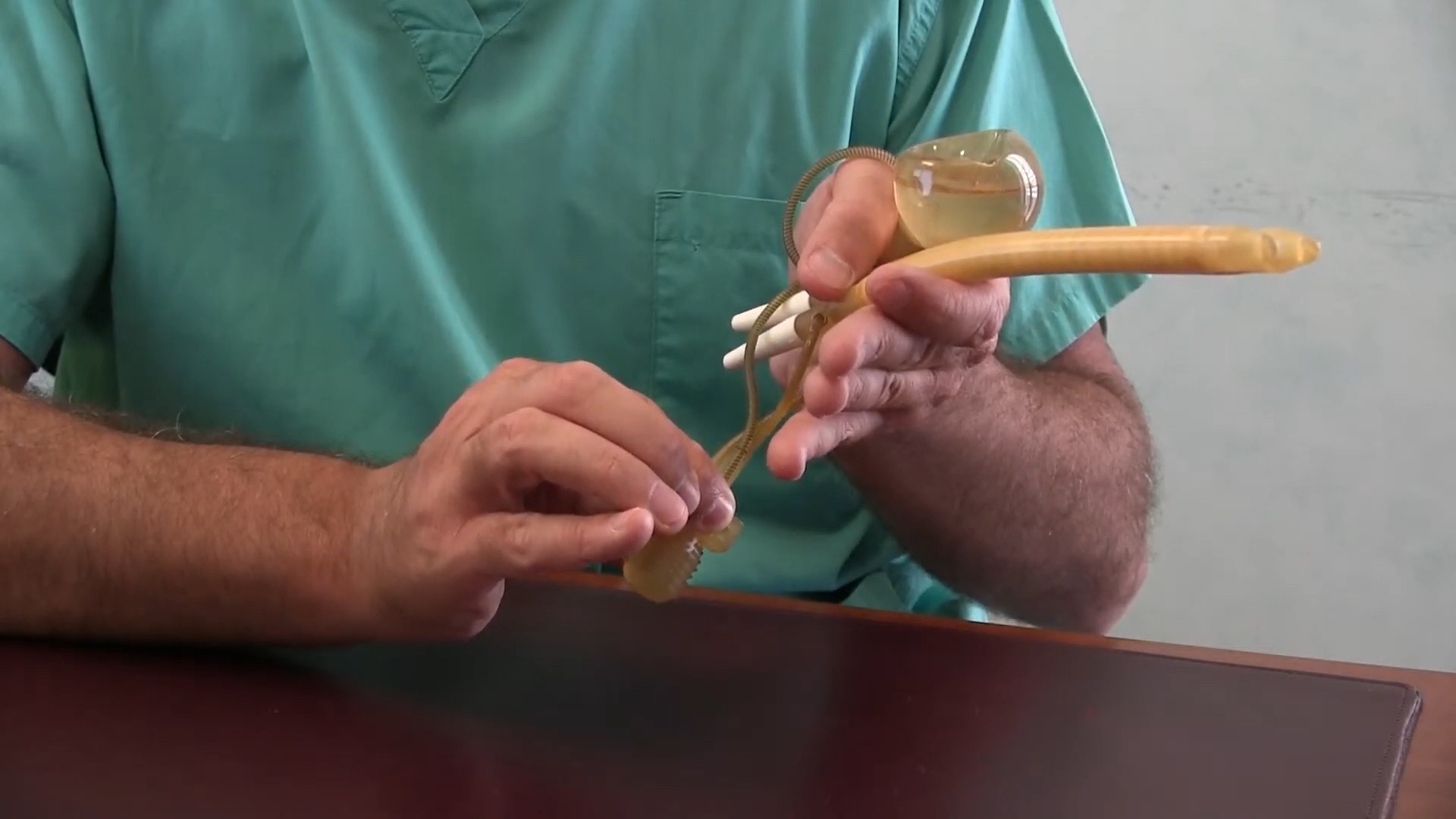
F.A.Q. Three-component Hydraulic Penile Prosthesis
How long does the hydraulic prosthesis procedure take?
The procedure usually takes between 20 and 30 minutes.
How many follow-up appointments are needed after the procedure?
The stitches can be removed 7-10days after the procedure. You will be given further instructions at that time. As soon as you are fully able to use the device without discomfort, you can resume sexual activity (at 6-8 weeks).
How long does the internal penile pump last (inflatable penile prosthesis)?
The prosthesis usually lasts 15 years, on average, but durations of up to 18-20 years have been recorded. The prosthesis includes a lifetime guarantee by substitution.
Will I maintain normal sensitivity after the procedure?
Sensitivity is not affected. You will have the same sensations you had prior to the procedure, which means that you will also be able to have a normal orgasm.
Can the procedure only be performed in hospital or can it also be carried out as a day surgery?
This depends on the patient’s general condition. In any case, a night in hospital is recommended.
Is the procedure carried out under local or general anesthetic?
The preference is for spinal anesthesia since it allows for prolonged pain relief after the procedure is completed. It is also very safe and easy to perform by the anesthetist. However, the procedure can also be performed under general or epidural anesthesia. The decision is left up to the patient and anesthetist.
Have there ever been adverse reaction problems due to which it has been necessary to remove the prosthesis?
The body will not reject the device unless it is infected. The risk of infection is 1%. If infected, the entire device must be removed, the patient will have to take antibiotics and the device will be replaced with another temporary rigid implant.
Is circumcision necessary for the hydraulic prosthesis implantation procedure?
Circumcision is not necessary. We thus do not recommend circumcision and, in fact, we discourage it. It is only advisable to do the strictly necessary and indicated. When it comes to penile surgery, less is better.
I have heard of semi-rigid implants as an option. What are the differences between this treatment and the hydraulic prosthesis?
Rigid implants reached their peak use in the 70s prior to the introduction of inflatable devices. They remain the preferred implant of urologists who perform a very limited number of prosthesis implantation procedures each year. Semi-rigid prosthetics have various disadvantages which inflatable devices do not suffer from. Semi-rigid implants can give rise to suboptimal erections and the penis tends to rotate. These implants also make it difficult for the penis to become flaccid, which can be difficult to hide. Since the device is not flexible like an inflatable pump, a larger size is necessary to be inserted into the penis and this carries the risk of hemorrhage, hematomas, infection and the area of numbness is larger. The pain and discomfort associated with the procedure are much more pronounced with a rigid device than with an inflatable one. The pain lasts a lot longer, from 4-6 weeks post-procedure. Lastly, rigid prosthetics are more likely to extrude through the skin several years later, since they are always hard and thus apply constant pressure to the glans. Over time, the flesh of the glans above the tip of the device thins and loses sensitivity. Prof. Antonini prefers to reserve the use of this device for patients unable to activate the pump, either due to severe arthritis or neurological disorders, or for patients undergoing a revision due to infection, to act as a temporary stent with a view to maintaining the penis’ length and girth. A penis with an inflatable implant has a normal appearance and normal sensitivity, while a penis with a rigid penile implant has an abnormal appearance and abnormal sensitivity.
Will the pump insertion have any kind of negative impact on my physical activity?
Generally speaking, you will be able to carry out any kind of physical activity without limitations of any kind. Clearly, we recommend certain precautions as with any other procedure. If the activity in question in cycling then you will have to replace your bicycle seat with a larger one with a concave middle section. Swimming does not pose any problems.
Once the prosthesis has been implanted, will I have normal sperm ejaculation during sex? Does it have any effect on this?
Erection, orgasm and ejaculation are three independent functions. Men who are impotent due to vascular causes can still have an orgasm and ejaculate with a flaccid penis. As such, the recovery of erection thanks to the prosthesis in such patients will allow them to continue to have an orgasm and ejaculate. Some patients have become fathers thanks to the prosthesis.
Patients suffering from ED secondary to radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy lose the ability to have an erection and to ejaculate. In such cases, the patients will be able to have an erection and an orgasm, but not to ejaculate.
Is it possible to perform the artificial urinary sphincter and hydraulic penile prosthesis procedures simultaneously or one after the other?
Many of our patients undergo sphincter and penile prosthesis insertion at the same time. However, experience with these simultaneous procedures has shown that it is preferable to insert the penile prosthesis first, followed by the sphincter.
Diabetics are prone to infections and/or long healing times. Does this condition cause problems with the prosthesis implantation procedure?
Diabetic men under our care have fewer infections than non-diabetics. The reason for this is unknown. One explanation may be that diabetics have reduced blood flow to the penis and thus bleed less during the procedure. A collection of blood in the scrotal cavity increases the risk of infection and is less probable in patients with compromised circulation.
If the prosthesis does not work, is it removed or is there a corrective procedure which can be carried out before considering removal?
In expert hands, replacement of the prosthesis is much easier and causes much less discomfort. It is up to the surgeon to determine whether the device is malfunctioning or broken.
Are training courses on the use of the prosthesis offered?
The patient will return one week after the procedure to learn how to activate the device. They will first be taught how to deflate the device. Once they succeed, they will learn how to inflate it. It is not uncommon for patients to need several visits before learning how to use it.
Once the stitches are removed, a DVD and a brochure on how to use the device will be provided. The patient must watch the video and read the brochure before the next visit. They should not try to learn how to use the device on their own before consulting the doctor. The partner is always welcome.
Is there a preventative maintenance program to care for the prosthesis?
No maintenance is required.
Is there a minimum number of times per day, week or month that the prosthesis needs to be used in order to gain maximum efficiency or ensure its effectiveness?
No. The device can be used at any time and there is no maximum or minimum number of uses.
After a radical prostatectomy for cancer, can a man with a penile prosthesis achieve ejaculation?
After a radical prostatectomy, a man can have an orgasm without ejaculation. The liquid that normally comes out of the penis during orgasm is produced in the prostate and seminal vesicles, organs which are completely removed during the radical prostatectomy. Furthermore, a vasectomy is carried out during the prostatectomy procedure such that there is no sperm loss within the body.
Is the size of the erection the same with the implant and the injection to the penis?
The size of the erection with the implant is that of the flaccid penis held by the glans and stretched as much as possible. A penis with an implant will never be as small/short or soft as a penis without an implant.
What is Peyronie’s disease?
Peyronie’s disease is a term used to describe the presence of scar tissue in the penis. The scar tissue forms following damage to erectile tissue. The lack of blood flow, erectile nerve lesions and direct trauma to the penis are the commonest causes of damage to the penile tissues. This disorder is a common consequence of diabetes. In this scenario, the scarring is always permanent and irreversible, unlike the scarring that occurs in a fracture of or trauma to the penis (in patients with normal blood flow to the penis). Thus no medical treatment has been shown to be effective for removing scar tissue from the penis of men with diabetes.
Scarring within the penis alters its functionality (elasticity) and anatomy. The collection of blood during erection depends on tissue functionality and intact anatomy of the penis. Any alteration to the penile tissues will lead to venous losses during erection.
What are the possible risks, side effects and complications of penile implants?
Infections, erosion of the prosthesis through the skin, urethra, small intestine or colon, lesions to the arteries or veins of the lower limbs, severe fleeting pain in the surgical area and mechanical problems with the implant.
Another consequence of the implant is a loss of the remaining spontaneous erection capacity. Patients who have functional spontaneous erections must be aware of this.
Other general risks inherent to any kind of surgical procedure, such as a bad reaction to anesthesia, pneumonitis if the procedure is carried out under general anesthetic, phlebitis or other risks stemming from pre-existing heart problems are other potential complications.
Furthermore, it may be necessary to have another surgical procedure in the event of complications or dissatisfaction with the initial implant.
What happens if I contract an infection?
Should an infection arise after insertion of the prosthesis, the patient must be admitted to the hospital and the device removed completely. Another device can immediately be re-inserted in parallel to the removal of the infected device. This operation is performed so as to avoid the shrinking and scarring of the penis that occurs following the infection of a penile implant. If it is not possible to identify the type of bacteria causing the infection, the patient will need 2-3 weeks of intravenous antibiotics. If another device is not immediately re-inserted, a second device may be implanted in the future. However, in addition to having the consequence of a much shorter penis, the procedure is much more difficult and the risk of patient dissatisfaction is higher. Given that infections are rare, post-infection re-implantation must only be carried out by highly experienced surgeons and not by surgeons with little or no experience.